Physical cross-border transportation
Physical cross-border transportation of currency or bearer negotiable instruments or precious stones and metals including gold, diamond and jewellery or any goods of high value including work of arts
Physical cross-border transportation means any in-bound or out-bound or in transit physical transportation of goods and includes physical transportation by a natural person or in that person’s accompanying luggage, shipment through containerized cargo, or mailing by a natural or legal person.
-
Section 131A of the Customs Act and Regulations 80 and 81 of the Customs Regulations 1989 make provisions that any person, whether incoming, outgoing or in transit, making a physical cross-border transportation of currency or bearer negotiable instruments (BNI) or precious stones and metals including gold, diamond and jewellery or any goods of high value including work of arts of an amount of more than 500,000 Mauritian rupees or its equivalent in foreign currency, needs to make a declaration to Customs.
-
Any person who needs to make a declaration to Customs shall –
-
submit the duly filled-in Declaration Form (MRA/CUS/CANS/AMLU/FORM 1) available at the Customs counter at the Airport, Port or Cargo Terminal; or
-
make an online declaration, related to physical cross-border transportation, through the MRA website: www.mra.mu under the e-services-Customs menu : https://eservices16.mra.mu/Currency/Index.jsp
-
In case of reasonable suspicion under this section of the law, a Customs officer may require any person to make a declaration as per paragraph (B).
Any person making a declaration may be questioned by a Customs Officer on the particulars of the declaration made and in the course of any questioning, the officer may inspect the person’s travel documents, passport, laissez-passer, tickets and accompanying luggage. The officer may also under reasonable cause, detain and search the person in accordance with Section 132 of the Customs Act.
Any person who fails to make a declaration or when so required, refuses to make a declaration or makes a declaration which is false or misleading in any material particular or without any reasonable excuse refuses to answer questions, shall commit an offence and on conviction shall be liable to a fine of not less than 20 per cent of the whole amount which is the subject matter of the offence but not exceeding 2 million rupees and to imprisonment for a term not exceeding 5 years.
Any person who wishes to have additional information relating to physical cross-border transportation may access the following link: https://eservices16.mra.mu/Currency/Index.jsp
Updated Information for Customs
-
Harmonised System for the Classifcation of goods version 2012 - Correlation Table
-
Physical Cross Border Transportation of Currency or Bearer Negotiable Instruments
-
Information to Stakeholders
10.30 Press Conference held by the Director General of MRA in the presence of the Commissioner of Police, Manufacturers and Traders in Cigarettes on 09.09.2006. Mr Cunningham made the following presentation - Launching Campaign to Combat Illicit Trade in Tobacco Products (1.45 MB)
-
Application Form for Registration of Manufacturers
This form is used for the registration of maunufacturers claiming duty exemption including ITem E70 of Unclassified Exemptions from Customs Duty (Part II of 1st Schedule to the Customs Tariff Act)
-
For manufacturers applying for registration under Item 9 of Part I (a) of the First Schedule to the Excise Act - gas oil used in stationary engines and boilers (SEBS):
The following forms and guidelines are applicable :-
-
Duty exemption to the manufacturing sector (MRA/CUS/DR/EMU/Form 4)
Securities / Bank Guarantees
Bank guarantee / security shall be required for the following reasons:
- For covering excise duty on excisable goods stored at the manufacturer's premises (security/bank guarantee in such amount as the Director-General may require);
- For securing payment of excise duty due (deferred payment) and for ensuring compliance with the Excise Act (bank guarantee in such amount as the Director-General may deem necessary);
- For exportation of excisable goods on which duty has not been paid – to ensure that the goods are exported as directed;
- Possession of a water still duly registered (Bank guarantee/Bond for the sum of Rs 10,000 per still shall be required).
Introduction to Customs
The MRA Customs falls under the umbrella of the Mauritius Revenue Authority (MRA). MRA falls under the aegis of the Ministry of Finance and Economic Development and the main function is to administrate the revenue laws.
In line with MRA strategic objectives, the Customs collects revenue for the government, ensures national security, protects the society and prevention of illicit financial flows while facilitating the legitimate movement of people and goods across the border.
All efforts are geared towards managing the Customs functions effectively and efficiently with the optimum use of risk management, automation and post control audit for the:
-
interception of smuggled and contraband goods such as illicit drugs;
-
inspection of travellers and their baggage, cargo and mail;
-
use of Non-Intrusive Inspection Technology such as X-Ray scanners and K-9;
-
assessment and collection of Customs duties, excise duties, VAT and other taxes levied under customs laws;
-
protection of the society against Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) infringed goods;
-
promotion of trade across borders by providing trade facilitation measures for legitimate trade;
-
enforcement of import and export restrictions and prohibitions;
-
collection and compilation of accurate import and export data; and
-
control of physical cross border transportation of currency or bearer negotiable instruments or precious stones and metals including gold, diamond and jewellery or any goods of high value including work of arts.
For an effective and efficient border control, MRA Customs works in close collaboration with the other government agencies namely, the Ministry of Agro-Industry and Food Security, the Ministry of Health and Quality of Life, the Government Pharmacist, the Veterinary Services, the Mauritius Police Force, etc.
MRA Customs has a work force of 646 officers who are posted at various customs offices, that is, the headquarters, airport, port, Rodrigues outstation and other custom controlled area.
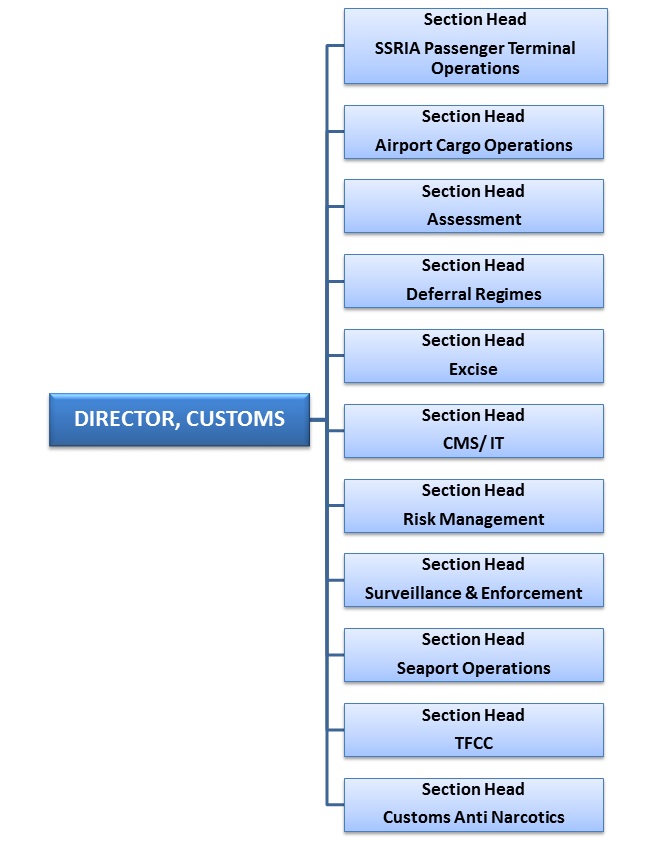
Customs has eleven sections. Each section has several interconnected operational units. A Section Head is responsible for the administration of each section. The main units and sub-sections falling under each section are listed below:
| 1. | Air Cargo Operations |
|
| 2. | Trade Facilitation, Customs Cooperation |
|
| 3. | Seaport Operations |
|
| 4. | Customs Management System / Information Technology (CMS / IT) |
|
| 5. | Assessment |
|
| 6. | Excise |
|
| 7. | Surveillance & Enforcement |
|
| 8. | Deferral Regimes |
|
| 9. | Risk Management |
|
| 10. | Airport Passenger Terminal (SSR) |
|
| 11. | Customs Anti-Narcotics |
|
Customs has three basic functions:
-
Fiscal function – consists of collecting and protecting government revenue in the form of customs duty, excise duty, VAT and other taxes under Customs Laws.
-
Protection / security function – ensures the security and protection of the country against transnational crimes and acts of terrorism. For instance, preventing prohibited goods, money laundering, illicit chemical, biological, radioactive and nuclear goods from entering the country, reducing the ability of terrorist groups to obtain precursor chemicals to make improvised explosive devices and to acquire light arms and weapons.
-
Economic function – provides trade facilitation measures for legitimate trade across the border in order to boost up import/ export and promote foreign direct investment. Reduce cost and dwell time, thereby ensuring fluidity and security to the business community in the Customs clearance.
During the last decade, there has been an evolution in the roles of Customs. In fact, the fiscal function which was considered to be the main mission of Customs has been coupled by other functions. Nowadays, the economic mission is considered to be an important function together with the security/protection function. These two functions when performed effectively contribute to attracting trade and investment.
On the other hand, with the reduction and/or elimination of tariff barriers, the revenue collection in terms of Customs duty has subsided. Modern Customs is, considered as an economic partner stakeholders and needs to strike the right balance between trade facilitation and control.
To accomplish its functions effectively and efficiently, Customs resorts to the following control methods and techniques:
-
Risk-Management and Intelligence
The use of advance electronic information on cargo and passengers and intelligence available to customs allows to enhance their profiling and targeting methods. This provides Customs the ability to focus on high-risk consignments and passengers.
-
Enforcement of Customs Laws
Customs ensures compliance to Customs laws through examination, query, post control audit and investigation with respect to all economic operators engaged in trade across the border. Some of the most common areas that are investigated by Customs are listed below:
- Drugs
Customs ensures border control to prevent drugs smuggling and drug-related offences. Its objective is to combat drug trafficking and physical cross border transportation of currency or bearer negotiable instruments or precious stones and metals including gold, diamond and jewellery or any goods of high value including work of arts of an amount of more than 500,000 rupees or such other amount as may be prescribed or its equivalent in any foreign currency through intelligence-led enforcement operations. Customs makes use of risk management, scanners and drug detector dogs to intercept contrabands. It also works in close collaboration with Mauritius Police Force (ADSU), Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU), NGOs and other intelligence and enforcement bodies specialized in combatting illegal drugs and money laundering to effectively fulfil its mission.
- Frauds
Customs investigates suspected cases where importers have deliberately evaded duty and/or VAT. This can be done both at clearance time of the cargo as well as after clearance through Post-Control Audit.
- Prohibited Goods
Customs also enforces prohibition and restriction of goods at import and export under other enactments in order to protect the society, and below are the main areas where such control is effected:
-
infringement of intellectual property rights – counterfeit, trademark and copyright goods
-
publications and goods of obscene character - child pornography, bestiality, sexual violence, etc.
-
firearms and offensive weapons
-
other import and export restrictions and prohibitions under other national legislations.
-
- Drugs
-
Wildlife Protection
Customs is also engaged in the protection of wildlife species through the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (C.I.T.E.S). The signatories of this convention are committed to the detection and prevention of trade in endangered species. It is a joint initiative of Customs and the National Parks & Conservation Service. Customs has been assigned the responsibility for the prevention of illegal trade in fauna and flora involving import, export and transit.
The Excise Section is responsible for the protection and collection of excise duty, monitoring and control and delivery of locally manufactured excisable goods (including plastic carrier bags and plastic pet bottles as from July 2006). As a result Customs has as main role the supervision, monitoring and control of excise operations which includes processing, blending, bottling, warehousing, ex-warehousing, etc. The list below points out the excise operations that need customs supervision and/or authorization.
-
The manufacture and removal/transfer of excisable goods such as perfumed spirits and denatured alcohol.
-
The transfer and the fixing of a still.
-
The placement and replacement of a seal on a still.v
-
Customs also perform Post Control Auditing on the operations of the manufacturers of alcoholic products, plastic carrier bags and plastic pet bottles to verify the Stock Book of finished product, material used, and any waste that result from production.
FAQ's - Visiting Crafts
- I am the owner of a yacht, I want to know whether there is any charges imposed by customs or other authorities for boarding purposes?
No charge is imposed by Customs for the clearance of incoming and outgoing yachts.
Kindly refer to Protocol for entry and departure of Vessel in Port Louis available on the MPA website on the following link http://www.mauport.com. -
Is it essential for me to wait for the Health and Quarantine officer in the yacht?
Yes, before boarding by the Health Officer boarding it is recommended the Master and every crew member/passenger to remain on board.
-
Is it important to mention the previous ports where I have called?
It is important to mention your previous port you have called when making the declaration through either your appointed agent or the harbour Radio who will insert your arrival credentials in the VCS (Vessel Clearance System).
-
After Customs clearance from the port of entry, can I go anywhere in Mauritius?
Any yacht once cleared by all authorities is allowed to leave port and move to any other mooring place around the island. However, the duration of stay and place of stay will have to be clearly indicated on the Declaration by Master/Owner of Pleasure Boat- Form 20 which shall be approved by the Boarding officer and handed over to the yacht master/owner at time of boarding.
Customs must be notified of any change in the duration of stay and a mail must be sent on the following address:
-
What is the maximum amount of days may I stay in Mauritius with my Yacht?
Any foreign yacht is allowed to stay for a period of 3 months as from date of arrival. A security in form of a Bank guarantee or office cheque to cover the duties, taxes as per Regulation 26 of the Customs Regulation will have to be submitted if the Yacht will stay beyond 3 months.
If a pleasure boat fails to leave Mauritius at the expiry of the authorised period then the security/bank guarantee shall be realised.
-
Is a manifest report necessary if a ship/aircraft does not have any Cargo destined for Mauritius?
Yes, a manifest report from the port of loading should be submitted to Customs even if none of the goods on board is destined for Mauritius.